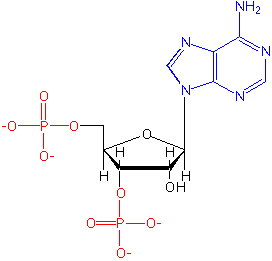
Nucleic acids are polymers, the monomeric unit being a nucleotide
that consists
of three basic elements:
-
A pyrimidine or purine base. There are typically only four different bases
in either DNA or RNA. In addition to the contents of Cytosine (C),
Guanine (G) and Adenine (A), the only difference between DNA and RNA is that
DNA contains thymine (T) and RNA uracil (U).
- A sugar residue: beta-D-Ribose in RNA compounds and 2"-Deoxy-beta-D-Ribose in DNA
compounds
- Phosphodiester linkages between 3' and 5' positions of
sugar moieties.
|
|