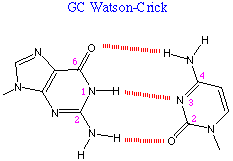
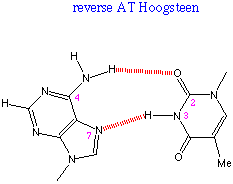
Nucleic acids differ one from another by the sequence of the bases. DNA is usually double-stranded, the two chains being anti-parallel. The strands are coiled in the form of a double-helix.The proportion of the bases in DNA is such that A=T and G=C. This is in accord with the fact that A hydrogen bonds with T and G hydrogen bonds with C in the so-called base-pairing: