


Carbohydrates play an important role in many biological processes
as energy-storage compounds and also in many recognition functions.
- Simple sugars of five (pentoses) and six (hexoses) carbon centers
are termed monosaccharides and they are chiral molecules
in which the D-form predominates in mammalian carbohydrates.
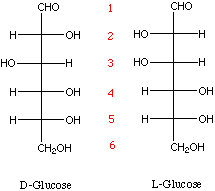
- Aldose are monosaccharides having and aldehid group whereas Ketoses
have a ketone group. Examples:
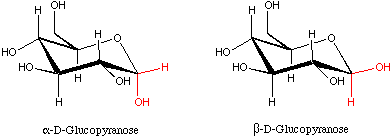
- Anomers are pairs of sugar molecules differing only in
one specific center, for instance alpha- and beta-glucose.
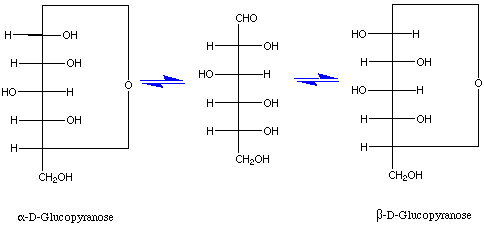
- The open-chain
form aids to understanding
the mutarotational process, in which two anomers interconvert spontaneously.
They can exist as
an equilibrium between the open-chain form and as
six-membered (pyranose) and/or five-membered (furanose) ring.
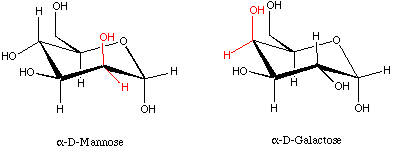
- Epimers are
isomers that differ in the configuration of one center, for instance,
alpha-glucose vs alpha-galactose (C-4 carbon) or alpha-glucose vs alpha-mannose
(C-2 carbon).
- Modified monosaccharides: