
 Autorelaxation
rates
Autorelaxation
rates
Autorelaxation rates for an IS spin system as a function of
DD (d) and CSA relaxation effects (c):
|
Autorelaxation
Rates
|
J(0)
|
J(wS)
|
J(wI-wS)
|
J(wI)
|
J(wI+wS)
|
ro
longitudinal
|
ro
transversal
|
|
RS(Sz)
|
0
|
3d+c
|
d
|
0
|
6d
|
0
|
0
|
|
RS(Sx)
|
2d+(2c/3)
|
(3d+c)/2
|
d/2
|
3d
|
3d
|
0
|
0
|
|
RI(Iz)
|
0
|
0
|
d
|
3d
|
6d
|
1
|
0
|
|
RI(Ix)
|
2d
|
3d
|
d/2
|
3d/2
|
3d
|
0
|
1
|
|
RIS(2IzSz)
|
0
|
3d+c
|
0
|
3d
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
|
RIS(2IzSx)
|
2d+(2c/3)
|
(3d+c)/2
|
d/2
|
0
|
3d
|
1
|
0
|
|
RIS(2IxSz)
|
2d
|
c
|
d/2
|
3d/2
|
3d
|
0
|
1
|
|
RIS(2I1S1)
|
2c/3
|
(3d+c)/2
|
0
|
3d/2
|
6d
|
0
|
1
|
|
RIS(2I1S-1)
|
2c/3
|
(3d+c)/2
|
d
|
3d/2
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
(from 94METH563)
where 
Thus, for instance, the following equations can be derived
from the above table:
-
Longitudinal Relaxation Rates: RN(Nz)

-
Transverse Relaxation Rates: RN(Nx,y)
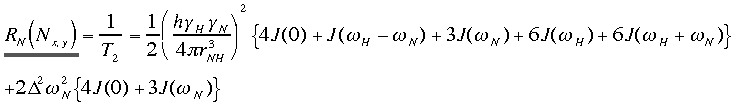
-
Cross-relaxation 1H-15N rate:
RN(Hz __>
Nz)
